Algorithms practice:leetcode 33 Search in Rotated Sorted Array
Description
There is an integer array nums sorted in ascending order (with distinct values).
Prior to being passed to your function, nums is possibly rotated at an unknown pivot index k (1 <= k < nums.length) such that the resulting array is [nums[k], nums[k+1], …, nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], …, nums[k-1]] (0-indexed). For example, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] might be rotated at pivot index 3 and become [4,5,6,7,0,1,2].
Given the array nums, after the possible rotation ,and an integer target, we need to return ,the index of the target ,if it is in nums, or -1 if it is not in nums.
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
Example
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0 Output: 4 Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3 Output: -1 Example 3:
Input: nums = [1], target = 0 Output: -1
Constraints
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000 -104 <= nums[i] <= 104 All values of nums are unique. nums is an ascending array that is possibly rotated. -104 <= target <= 104
solution
The ‘nums’ array may be rotated at an unknown pivot index ‘k’. Let me give you an example. Let say that we have an array with eight elements. the orginal array is [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]. The pivot index can be any number from 0 to 7. If the pivot index is zero then the array Doesn’t change/Remains the same. look at this picture.
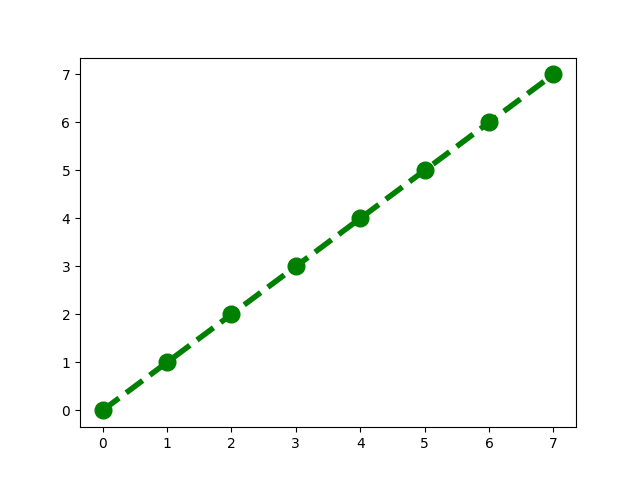
pivot is 1
If the pivot is one, then the rotated array looks like this.
the orginal array is [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. If we choose one as the pivot, then the rotated array looks like this. You can think of it as spliting the array into two parts from the pivot. And then we put the right part in front of the left part.
pivot index k = 1: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0
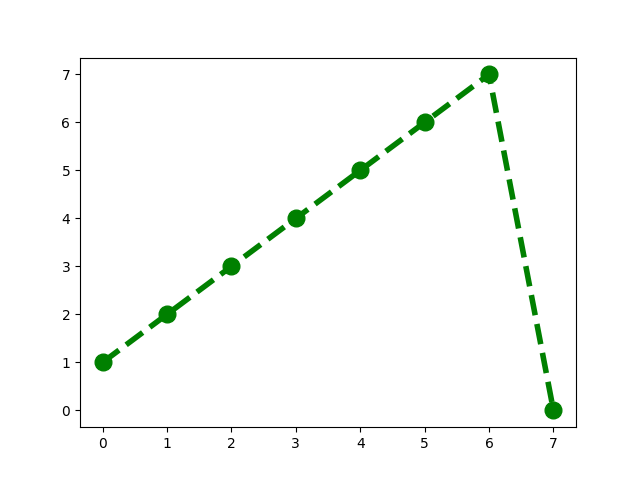
pivot is 2
If the pivot is two then the rotated array looks like this.
pivot index k = 2 : 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1
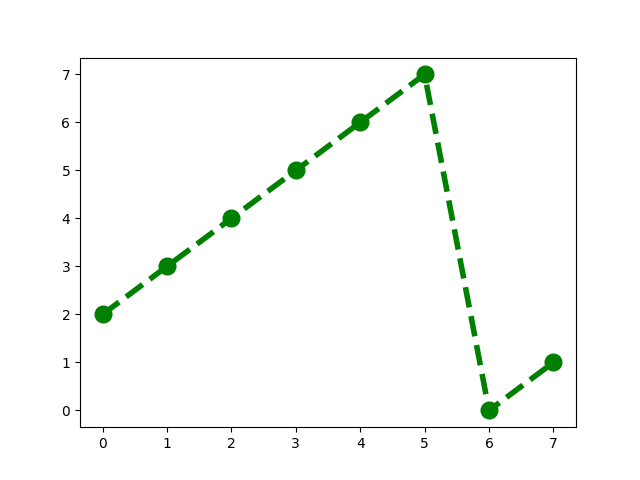 Now if the pivot is three, I want you to try to picture the rotated array in your head. if you have a piece of paper and a pen you can try to draw it. I will give you a second.
Now if the pivot is three, I want you to try to picture the rotated array in your head. if you have a piece of paper and a pen you can try to draw it. I will give you a second.
this is the rotated array.
Now are we clear on how to rotate an array?
### pivot is 3
pivot index k = 3: 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2
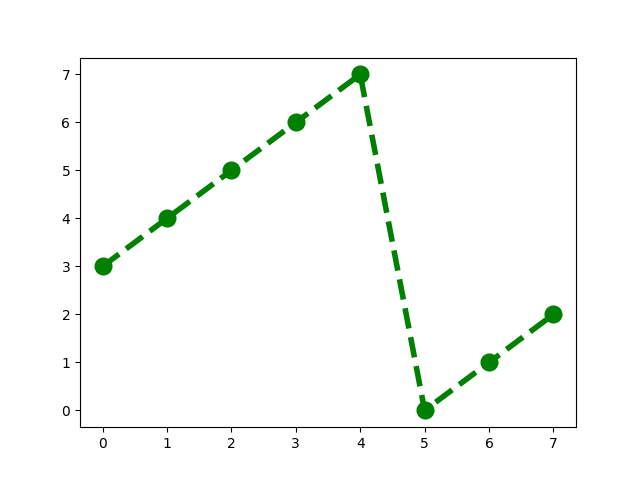
pivot index k = 4 : 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3
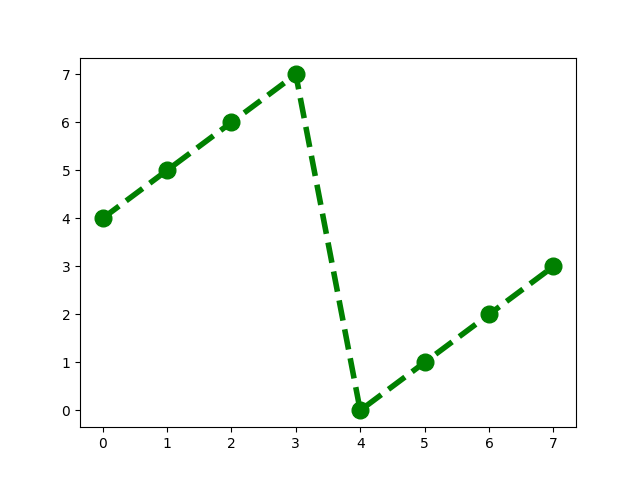
pivot index k = 5 : 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4
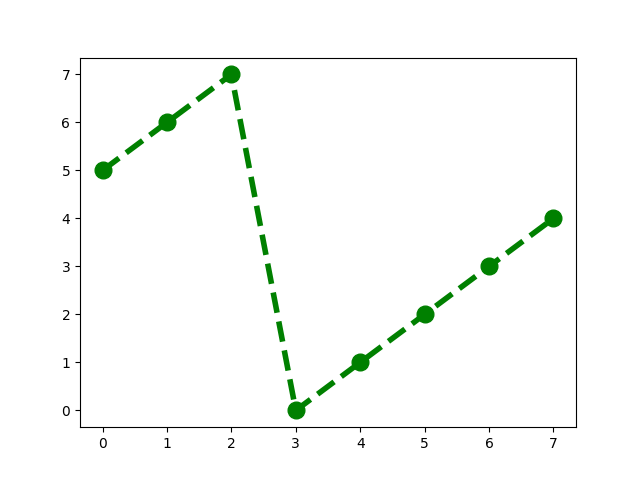
pivot index k = 6 : 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5
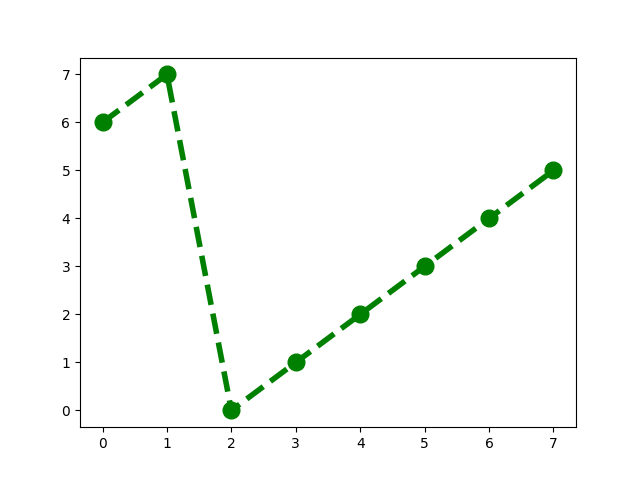
pivot index k = 7 : 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
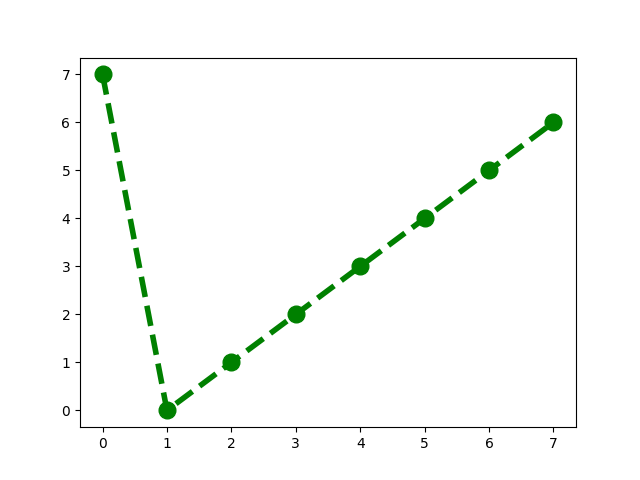
algorithm
we have to write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity, which can be achieved by using binary search. The main idea is to divide the search space into two halves from the middle. If the middle element is the target, the process terminates. If not, we decide which subarray to continue the search in (If not, we decide in which sub-array to continue the search.). The key to the problem is how to choose the subarray.
Now please take a closer look at this picture now I’m going to split the rotated array in half.
we can see the pivot index k = 2 and nums is [2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1], and the target is 3, Now let’s try to split this rotated array in half from the middle.
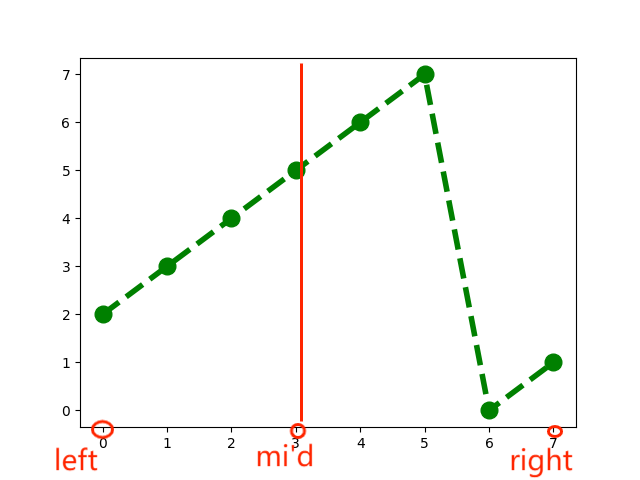 we select index 3 as the middle element.
The sub-array on the left is [2 3 4 5], and the sub-array on the right is [6 7 0 1].
we select index 3 as the middle element.
The sub-array on the left is [2 3 4 5], and the sub-array on the right is [6 7 0 1].
The left sub-array is in ascending order, and first we determine if the target is in this array.
if target >= nums[left] and target =< nums[middle]
if the target is larger than or equals nums[left] and smaller than or equals nums[middle], then we know the target can be found in this subarray.
In this case, our target is 3, which satisfies the conditions 2<3 and 3<5. Therefore, the target must be in this sub-array. So, we use this sub-array in the next iteration. Sometimes the target is not in the left subarray. in that case, we use the right sub-array in the next iteration. We will talk about what to do in that case later.
now we write the code: firstly, we declare two int variables as Pointers: a left pointer and a right pointer and assign 0 to the left pointer ,assign nums.size()-1 to the right pointer .
int left =0;
int right = nums.size()-1;
we use while loop to iterate the array. In each iteration , we first need to calculate the middle pointer as (left +right )/2 (divided by 2). If the middle element is the target, we return the index of the middle element. if not, we search the target in the subarray in asending order. how do we determine which one that is?
while(left<=right)
{
int mid = (left+right)/2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
{
return mid;
}
....
}
}
we first check the left one. if nums[left] <=nums[mid], then we know the elements in the left subarray are in asending order.
the next step is to check if the target is in it. If it is,We are gonna use the left subarray in the next iteration. that means we no longer need the right subarray, we can get rid of it by assign mid -1 to the right pointer.
if(nums[left] <=nums[mid]) // [left , mid] order subarray
{
if(nums[left] <=target && target< nums[mid])
{
right = mid-1;
}
else//( target> nums[mid] || target< nums[right])
{
left = mid+1;
}
}
if the target is not in the left subarray, Then it must be in the right one. that means we don’t need the left subway. so how do we get rid of it?
we can get rid of it by assign mid+1 to the right pointer.

In the scenario we just discussed, the left subarray is in Ascending order, Now let’s talk about what to do if the right sub array is in Ascending order.
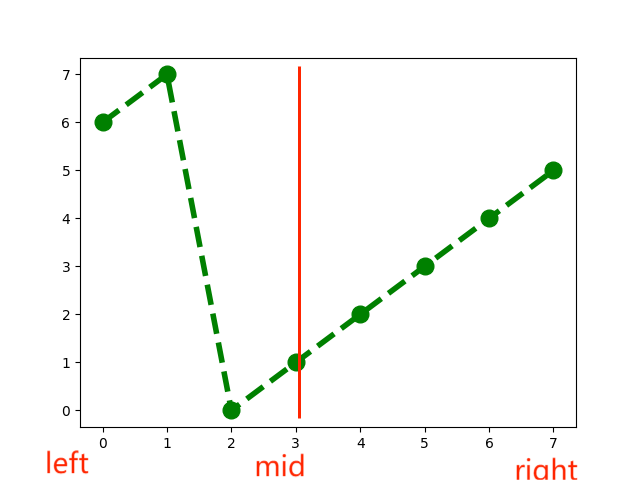
the next step is to check if the target is in it. if the target is larger than or equals nums[mid] and smaller than or equals nums[right], then we know the target can be found in this subarray. We are gonna use the right subarray in the next iteration. that means we no longer need the left subarray, we can get rid of it by assign mid +1 to the left pointer.
if the target is not in the right subarray, Then it must be in the left one. that means we no longer need the right subarray. we can get rid of it by assign mid-1 to the right pointer.
// [mid , right] order subarray
if(nums[mid] <target && target<= nums[right])
{
left = mid+1;
}
else //( target> nums[mid] || target< nums[right])
{
right = mid-1;
}
if the target is not in nums array, then we return -1 at the end.
code
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {//O(N) O(log(n))
int left =0;
int right = nums.size()-1;
while(left<=right)
{
int mid = (left+right)/2;
if (nums[mid] == target)
{
return mid;
}
if(nums[left] <=nums[mid]) // [left , mid] order subarray
{
if(nums[left] <=target && target< nums[mid])
{
right = mid-1;
}
else//( target> nums[mid] || target< nums[right])
{
left = mid+1;
}
}
else
{
// [mid , right] order subarray
if(nums[mid] <target && target<= nums[right])
{
left = mid+1;
}
else //( target> nums[mid] || target< nums[right])
{
right = mid-1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
words
-
integer [ˈɪntɪdʒə]: In mathematics, an integer is an exact whole number such as 1, 7, or 24 as opposed to a number with fractions or decimals.
i. In C++, there are different types of variables (defined with different keywords), for example: int - stores integers (whole numbers), without decimals, such as 123 or -123 double - stores floating point numbers, with decimals, such as 19.99 or -19.99
-
array [əreɪ]: An array of objects is a collection of them that is displayed or arranged in a particular way.
i. Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable, instead of declaring separate variables for each value.(C++ https://www.w3schools.com/cpp/cpp_arrays.asp)
-
ascending [əˈsɛndɪŋ] : If a group of things is arranged in ascending order, each thing is bigger, greater, or more important than the thing before it.
i. I shall list my objections to the plan in ascending order of importance.我将会把我反对这个计划的理由按重要性从小到大一一列出。
-
Descending [dɪˈsendɪŋ] : When a group of things is listed or arranged in descending order, each thing is smaller or less important than the thing before it.
i. The results, ranked in descending order (= from the highest to the lowest) are as follows: 结果按递减顺序排列如下。
-
distinct [dɪˈstɪŋkt]: values every element in the array is unique
i. C++ Program to Counting distinct elements in an array.
-
Prior [ˈpraɪər] : Referring to something that occurred or existed earlier in time or order within a computing context
i. The new software update will build upon the prior version’s functionalities.
-
rotate [roʊˈteɪt]: To turn or move around a central point
i. The function ‘rotateArray()’ rotates the elements of the array to the right by a given number of steps.
-
pivot [ˈpɪvət]: A fixed point supporting something that turns or balances.
i. QuickSort algorithm selects a pivot element to partition the array into smaller segments.
-
index [ˈɪndeks]: A numerical value that indicates the position of an element in a list or array.
i. Accessing elements in an array requires specifying the index of the desired element.
-
element [ˈɛlɪmənt]: An individual item in a larger set or sequence.
i. In Python lists, each element can be of any data type, allowing for versatility in programming.
-
time complexity [kəmˈplɛksəti]: The measure of the amount of time an algorithm takes to complete.
i. The time complexity of the algorithm determines how the execution time grows with the input size.
-
space complexity [kəmˈplɛksəti]: The measure of the amount of memory space an algorithm requires.
i. Analyzing space complexity is crucial to understand how much memory an algorithm requires.
-
divide [dɪˈvaɪd]: To separate something into smaller parts.
i. The merge sort algorithm divides the array into smaller sub-arrays for sorting.
-
split [splɪt]: To separate something into two or more parts.
i. The split operation in databases divides large tables into smaller ones for better management.
-
halve [hæv]: To separate something into two equal parts.
i. Binary search continuously halves the search space to find the target element efficiently.
-
iteration [ˌɪtəˈreɪʃən] : The repetitive execution of a set of instructions in programming, often achieved using loop statements.
i. The ‘for’ loop in Python allows for easy iteration over a list of items.
-
pointer [ˈpɔɪntər] : A programming concept that refers to a variable holding the memory address of another variable, enabling indirect access to that memory location.
i. In C programming, pointers are used extensively for memory manipulation.
-
initialize [ɪˈnɪʃəˌlaɪz] : The act of setting a variable or object to its initial state by assigning an initial value or configuration.
i. To avoid errors, always initialize variables before using them in a program.
-
declare [dɪˈklɛər]: To specify the type and identifier of a variable or symbol in programming.
i. You need to declare the variables at the beginning of the function in C++.
-
variables [ˈvɛriəblz] : Named containers in programming used for storing data values.
i. In Java, variables can hold specific types of data like numbers, strings, or objects.
-
assign [əˈsaɪn]: The action of associating a value with a variable or assigning a specific value or object to a variable.
i. The programmer will assign the value ‘true’ to the variable ‘isActive’.
-
terminate [ˈtɜrməˌneɪt] : To end the execution of a program or halt a process in computing.
i. If the condition is met, the system will terminate the execution of the loop.
-
binary [ˈbaɪnəri] search : A searching algorithm used to quickly find a target value in a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half.
-
pass:[pɑːs]: to give sth to sb by putting it into their hands or in a place where they can easily reach it
i. Pass by value means passing a copy of the variable to the method.
ii. Pass by reference means passing access to the variable to the method.
-
0-indexed: Zero-based array indexing is a way of numbering the items in an array such that the first item of it has an index of 0, whereas a one-based array indexed array has its first item indexed as 1.
-
iterate [ˈɪtəreɪt] :to repeat a ↑mathematical or ↑computing process or set of instructions again and again, each time applying it to the result of the previous stage
i. This code uses a ‘for’ loop to iterate over a list and print each element.
ii. It iterates through the list based on the index of each element, obtained using ‘range(len(list))’.
iii. It iterates from 1 to 4 and, in each iteration, prints the current number multiple times based on the iteration number.
link
- C++ Variables
- https://www.learncpp.com/cpp-tutorial/variable-assignment-and-initialization/
- https://www.codeease.net/programming/python/Declaration-and-Initialization-of-Variables
- https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/solutions/3879263/100-binary-search-easy-video-o-log-n-optimal-solution/
- https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/description/
撰稿人
yang, C, 斜阳